Introduction
Digital media production has fundamentally transformed the way we create, consume, and interact with content. In today’s digital age, media production encompasses a broad spectrum of activities. Visit
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- The Genesis of Digital Media Production
- Key Components of Digital Media Production
- Technologies Shaping Digital Media Production
- The Production Process in Detail
- The Role of Digital Media Production in Various Sectors
- Challenges in Digital Media Production
- Future Trends in Digital Media Production
- Conclusion
- FAQs
The Genesis of Digital Media Production
Digital Media Production has its origins in the technological advancements of the late 20th century. Before the digital era, media production relied heavily on analog methods—film, magnetic tape, and traditional photographic techniques. The transition to digital technologies revolutionized the field, making media creation more accessible and versatile. Read More

Early Developments
The journey began with the advent of personal computers and digital recording devices. In the 1980s, software like Adobe Photoshop and Final Cut Pro emerged, enabling creators to manipulate images and video with unprecedented ease. This period also saw the development of early digital audio workstations (DAWs), which allowed for more sophisticated sound recording and editing.
The Internet Era
The 1990s and early 2000s marked the rise of the internet, which drastically changed the landscape of digital media production. The proliferation of web-based platforms like YouTube and social media sites democratized content creation, allowing anyone with a camera and an internet connection to share their work with a global audience. This era also saw the introduction of user-friendly editing software and affordable digital cameras, further expanding the possibilities for amateur and professional creators alike.
Key Components of Digital Media Production
Digital media production involves several critical stages, each contributing to the creation of a final product. Understanding these components is essential for anyone looking to delve into the field.
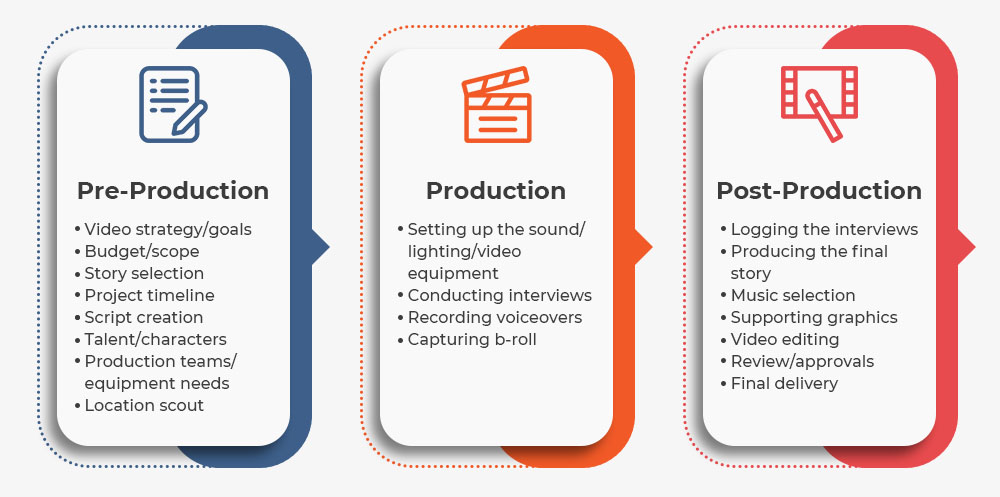
1. Pre-Production
In Digital Media Production Pre-production is the foundational stage where the concept and logistics of a project are developed. It is a crucial phase that sets the tone for the entire production process.
- Concept Development: This involves brainstorming and refining the central idea or message of the content. Whether it’s a marketing campaign, a short film, or an educational module, a clear concept is essential for guiding the project.
- Scriptwriting: A script outlines the narrative, dialogue, and structure of the content. It serves as a blueprint for the production phase, ensuring that all elements align with the original vision.
- Storyboarding: Storyboards are visual representations of scenes or sequences, providing a roadmap for how the content will unfold. They help in planning camera angles, movements, and transitions.
- Budgeting and Scheduling: Allocating resources and setting deadlines are critical for managing the production process efficiently. A well-planned budget and schedule help in avoiding delays and cost overruns.

2. Production
Digital Media Production: The production phase is where the content is created. This stage involves capturing raw footage, audio, and other media elements.
- Filming/Recording: Depending on the project, this could involve shooting video, recording audio, or both. The choice of equipment and techniques can significantly impact the quality of the final product.
- Directing: The director’s role is to guide the talent and crew, ensuring that the content is produced according to the vision and objectives. This involves directing actors, setting up shots, and overseeing the overall production.
- Lighting and Sound: Proper lighting and sound are essential for creating a professional-looking and sounding product. This includes setting up lighting equipment, microphones, and other audio-visual tools.

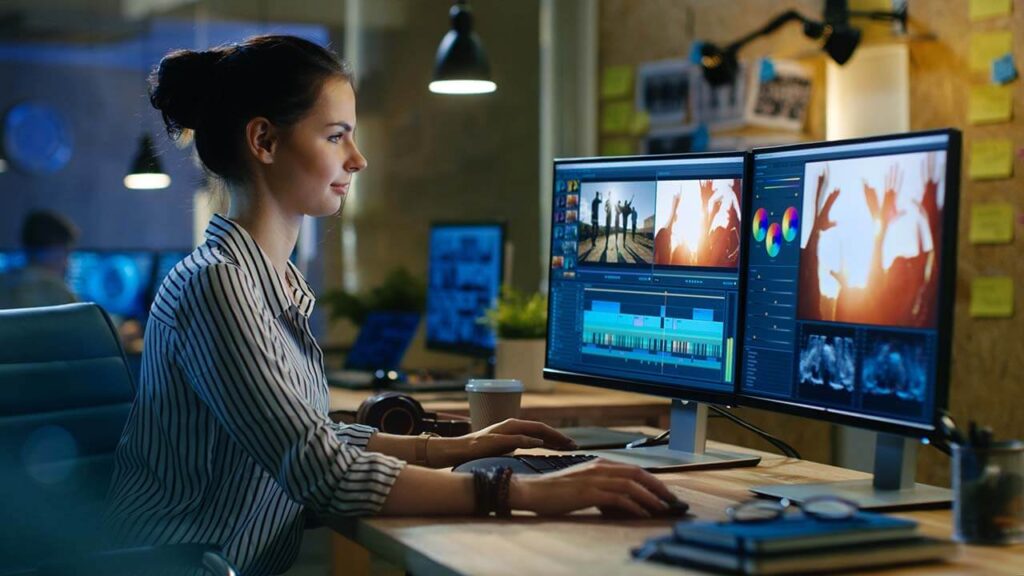
3. Post-Production
Digital Media Production: Post-production is where the raw materials are transformed into the final product. This stage includes several key activities:
- Editing: Editing involves cutting and arranging footage or audio to create a cohesive and engaging narrative. This can include trimming clips, adding transitions, and ensuring smooth flow.
- Visual Effects (VFX): VFX are used to enhance or alter the visual elements of the content. This could involve adding special effects, animations, or computer-generated imagery (CGI).
- Sound Design: Sound design includes mixing and mastering audio elements to ensure clarity and balance. This may involve adding sound effects, background music, and voiceovers.
- Color Grading: Color grading adjusts the color balance and tone of the footage to achieve a desired look. This process can enhance the mood and visual appeal of the content.
4. Distribution
Distribution involves delivering the finished product to the intended audience. This stage includes several methods:
- Publishing on Platforms: Content can be uploaded to platforms like YouTube, Vimeo, or social media sites. Each platform has its own requirements and best practices for content delivery.
- Broadcasting: Traditional broadcasting involves sharing content through television or radio channels. This method often requires compliance with industry standards and regulations.
- Streaming Services: Streaming platforms like Netflix, Hulu, and Amazon Prime offer opportunities for distributing video content on-demand. These services often involve partnerships and agreements.
- Physical Media: For some projects, physical media such as DVDs or Blu-rays may be produced. This method is less common today but still relevant for certain types of content.

Technologies Shaping Digital Media Production
Several technologies are instrumental in digital media production, each offering unique capabilities and advantages.
1. Digital Cameras
Digital cameras have revolutionized the way we capture images and video. Modern digital cameras offer high resolution, advanced features, and greater flexibility compared to their analog predecessors.
- DSLR Cameras: Digital Single-Lens Reflex (DSLR) cameras are popular for their versatility and image quality. They offer interchangeable lenses and manual controls, making them suitable for various types of media production. Learn more about DSLR cameras.
- Mirrorless Cameras: Mirrorless cameras offer a compact design and faster performance compared to DSLRs. They are known for their high-resolution sensors and advanced autofocus systems. Explore mirrorless cameras.
- Smartphone Cameras: With the advent of high-quality smartphone cameras, content creation has become more accessible. Modern smartphones offer features such as 4K video recording, advanced imaging sensors, and a range of editing apps. Check out smartphone camera reviews.

2. Editing Software
Editing software is essential for refining and enhancing media content. Several software options cater to different needs and skill levels.
- Adobe Premiere Pro: A leading video editing software used by professionals for its comprehensive features and integration with other Adobe products. Learn more about Adobe Premiere Pro.
- Final Cut Pro: Popular among Mac users, Final Cut Pro offers powerful editing tools and a user-friendly interface. Explore Final Cut Pro.
- DaVinci Resolve: Known for its advanced color grading capabilities, DaVinci Resolve is also a robust video editing tool. Discover DaVinci Resolve.

3. Audio Production Tools
Audio production tools are vital for creating and mixing sound. These tools range from professional DAWs to various plugins and effects.
- Pro Tools: Widely used in the music and film industries, Pro Tools offers comprehensive audio editing and mixing capabilities. Explore Pro Tools.
- Ableton Live: Known for its versatility and live performance features, Ableton Live is popular among electronic music producers. Learn about Ableton Live.
- Logic Pro: A powerful DAW for Mac users, Logic Pro provides extensive features for music production and sound design. Check out Logic Pro.

4. Graphic Design Software
Graphic design software is essential for creating visual elements, including graphics, layouts, and illustrations.
- Adobe Photoshop: A leading tool for photo editing and graphic design, Photoshop offers a wide range of features for manipulating images. Learn more about Adobe Photoshop.
- Adobe Illustrator: Ideal for creating vector graphics, Illustrator is used for designing logos, icons, and illustrations. Explore Adobe Illustrator.
- InDesign: Used for layout design, InDesign is popular for creating print and digital publications. Discover InDesign.

5. 3D Modeling and Animation
3D modeling and animation software enable creators to design and animate three-dimensional objects and environments.
- Blender: An open-source 3D modeling and animation tool, Blender offers a range of features for creating complex 3D content. Learn about Blender.
- Autodesk Maya: A professional 3D animation software used for film, television, and game development. Explore Autodesk Maya.
The Production Process in Detail
Each stage of the digital media production process involves specific tasks and considerations. Understanding these details can help creators manage their projects more effectively.
1. Pre-Production
- Concept Development: This phase involves defining the project’s goals, target audience, and key messages. It often includes brainstorming sessions and market research to refine the concept.
- **
Scriptwriting**: The script serves as a detailed guide for the production, outlining the dialogue, actions, and scenes. It may undergo multiple revisions before finalization.
- Storyboarding: Storyboards help visualize the content, allowing creators to plan camera angles, movements, and transitions. This helps in identifying potential issues and streamlining the production process.
- Budgeting and Scheduling: Creating a detailed budget and schedule ensures that resources are allocated efficiently. This includes estimating costs for equipment, personnel, locations, and other expenses.
2. Production
- Filming/Recording: The production team captures the raw footage and audio based on the script and storyboard. This stage involves setting up equipment, directing talent, and managing the production environment.
- Directing: The director guides the creative aspects of the project, ensuring that the performance, visuals, and audio align with the vision. This may involve directing actors, adjusting camera angles, and making real-time decisions.
- Lighting and Sound: Proper lighting and sound setup are crucial for achieving high-quality media. This includes positioning lights, setting up microphones, and managing sound levels to avoid distortion.
3. Post-Production
- Editing: During editing, the raw footage is cut and arranged to create a cohesive story. This involves trimming unnecessary clips, adding transitions, and ensuring a smooth flow.
- Visual Effects (VFX): VFX enhance or alter the visual elements of the content. This can include adding animations, special effects, and CGI to achieve the desired look.
- Sound Design: Sound design involves mixing and mastering audio elements to achieve clarity and balance. This includes adding sound effects, background music, and voiceovers to enhance the overall experience.
- Color Grading: Color grading adjusts the color balance and tone of the footage to create a specific mood or style. This process enhances the visual appeal and ensures consistency across scenes.
4. Distribution
- Publishing on Platforms: Content is uploaded to various platforms based on the target audience. This includes optimizing content for each platform’s requirements and best practices.
- Broadcasting: Traditional broadcasting involves distributing content through television or radio channels. This method often requires compliance with industry standards and regulations.
- Streaming Services: Streaming platforms offer on-demand content delivery, allowing viewers to access content anytime. This involves working with streaming services to meet their content and technical requirements.
- Physical Media: Producing physical media such as DVDs or Blu-rays involves additional steps, including mastering, replication, and packaging. This method is less common but still relevant for certain types of content.
The Role of Digital Media Production in Various Sectors
Digital media production has a profound impact on multiple sectors, each benefiting from the advancements in technology and media creation.
1. Entertainment
In the entertainment industry, digital media production is at the heart of creating movies, television shows, and online content. Advances in technology have enabled more complex and visually stunning productions.
- Film Production: Digital cameras and editing software have revolutionized film production, allowing for higher-quality visuals and more efficient post-production processes. Explore trends in film production.
- Television: Television production has also benefited from digital advancements, with high-definition and 4K content becoming the norm. Learn about television production trends.
- Online Content: Platforms like YouTube and Netflix have transformed how content is created and consumed. Creators can now reach global audiences with original content. Check out online content trends.
2. Advertising and Marketing
Digital media production plays a critical role in advertising and marketing, with high-quality media enhancing brand visibility and engagement.
- Promotional Videos: Companies use promotional videos to showcase their products and services. These videos often include professional editing, graphics, and sound design to attract and engage viewers. Learn more about video marketing.
- Social Media Content: Engaging social media content helps brands connect with their audience. This includes creating visually appealing posts, videos, and interactive elements. Explore social media content strategies.
- Interactive Advertisements: Interactive ads, such as clickable videos and augmented reality experiences, offer innovative ways to engage potential customers. Discover interactive advertising trends.
3. Education
In education, digital media production is used to create instructional videos, e-learning modules, and interactive content, making learning more engaging and accessible.
- E-Learning Modules: Interactive e-learning modules include multimedia elements such as videos, quizzes, and animations to enhance the learning experience. Check out e-learning trends.
- Instructional Videos: Educational videos provide visual explanations of complex concepts, making it easier for students to understand and retain information. Explore instructional video resources.
- Virtual Classrooms: Virtual classrooms use video conferencing and digital media to facilitate remote learning. This has become increasingly important for distance education and online courses. Learn about virtual classroom technologies.
4. Corporate Communication
Companies use digital media production for internal and external communications, including corporate videos, training materials, and promotional content.
- Corporate Videos: Corporate videos are used for a variety of purposes, including company profiles, training, and internal communications. Read about corporate video production.
- Training Materials: Digital media is used to create interactive training materials that enhance employee learning and development. Discover corporate training resources.
- Promotional Content: Companies create promotional content to market their products and services, using digital media to reach a broader audience and drive engagement. Explore promotional content strategies.
5. Social Media
Social media platforms rely heavily on digital media production for user-generated content, influencer marketing, and promotional campaigns. Engaging media content is key to capturing audience attention on social networks.
- User-Generated Content: Social media users create and share their own content, including photos, videos, and stories. This content can significantly influence brand perception and engagement. Learn about user-generated content.
- Influencer Marketing: Influencers create content to promote brands and products, leveraging their followers and credibility. This form of marketing relies on high-quality media production to attract and retain audience interest. Check out influencer marketing strategies.
- Promotional Campaigns: Brands use social media for targeted advertising and promotional campaigns. This includes creating engaging visuals and videos to capture audience attention. Explore social media advertising.
Challenges in Digital Media Production
Despite its many advantages, digital media production faces several challenges that can impact the quality and effectiveness of content.
1. Technological Advancements
The rapid pace of technological advancements can be both an opportunity and a challenge. Staying up-to-date with the latest tools and techniques requires continuous learning and adaptation.
- Keeping Up with Changes: New technologies and software updates can make existing tools obsolete. Creators must invest time and resources in learning and adapting to new technologies. Read about technology trends.
- Cost of Upgrades: Upgrading equipment and software can be costly. Balancing the need for the latest technology with budget constraints is a common challenge. Explore budgeting for tech upgrades.
2. Quality vs. Quantity
The demand for constant content updates can lead to a focus on quantity over quality. Striking a balance between producing frequent content and maintaining high standards is essential.
- Maintaining Standards: Ensuring consistent quality while meeting content production deadlines requires effective planning and resource management. Learn about content quality management.
- Avoiding Burnout: The pressure to produce large volumes of content can lead to burnout among creators. Managing workload and prioritizing self-care is important for sustaining creativity and productivity. Read about preventing burnout.
3. Intellectual Property
Protecting intellectual property is a critical concern in digital media production. Unauthorized use and piracy can undermine the value of original content.
- Copyright Protection: Ensuring that content is protected by copyright helps prevent unauthorized use and distribution. Creators should be aware of copyright laws and registration processes. Explore copyright protection.
- Digital Rights Management (DRM): DRM technologies can help control how digital content is used and shared, though they are not foolproof. Learn about DRM solutions.
Future Trends in Digital Media Production
The future of digital media production is shaped by emerging technologies and evolving consumer preferences. Understanding these trends can help creators stay ahead of the curve.
1. Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR)
VR and AR technologies are creating new opportunities for immersive experiences and interactive content.
- Virtual Reality: VR offers fully immersive experiences by creating virtual environments that users can interact with. This technology is used in gaming, training simulations, and virtual tours. [Explore VR applications](https://www.the
verge.com/virtual-reality).
- Augmented Reality: AR overlays digital content onto the real world, enhancing user experiences through interactive elements. AR is used in applications such as mobile games, retail experiences, and navigation. Learn about AR innovations.
2. Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI is increasingly being used to enhance various aspects of digital media production, from content creation to audience analysis.
- AI in Content Creation: AI tools can automate tasks such as video editing, image enhancement, and audio processing, improving efficiency and creativity. Discover AI in media production.
- AI-Powered Analytics: AI can analyze audience data to provide insights into content performance and preferences, helping creators make data-driven decisions. Read about AI in analytics.
3. Interactive and Personalized Content
Consumers increasingly expect content that is interactive and tailored to their preferences.
- Interactive Content: Interactive content, such as quizzes, polls, and clickable videos, engages users by allowing them to participate actively. Learn about interactive content strategies.
- Personalized Experiences: Personalization involves tailoring content to individual user preferences and behaviors, enhancing relevance and engagement. Explore personalization techniques.
Conclusion
Digital media production continues to evolve, driven by technological advancements and changing consumer expectations. From its early days of analog methods to today’s sophisticated digital tools, the field has made significant strides. Understanding the core components, technologies, and trends in digital media production can help creators and businesses navigate this dynamic landscape and produce high-quality, impactful content.
As we look to the future, embracing emerging technologies such as VR, AR, and AI will be crucial for staying competitive and innovative. By staying informed and adaptable, digital media professionals can harness the full potential of these advancements to create engaging and meaningful experiences for their audiences. For More Info
External Links:
- Adobe Premiere Pro
- TechRadar: Best Mirrorless Cameras
- DaVinci Resolve
- Blender
- Social Media Examiner: User-Generated Content Marketing
- Forbes: How AI is Transforming the Media Industry
FAQs
Q1: What is digital media production?
Digital media production refers to the creation, manipulation, and distribution of content using digital technologies. This includes a wide range of media such as video, audio, graphics, animations, and interactive content. The process typically involves several stages, including pre-production (planning and scripting), production (capturing raw materials), and post-production (editing and refining the content).
Q2: What are the key stages of digital media production?
The key stages of digital media production are:
Pre-Production: Involves planning, scripting, storyboarding, and organizing resources.
Production: Includes capturing video footage, recording audio, and other media creation tasks.
Post-Production: Entails editing, adding visual effects, sound design, and color grading.
Distribution: Focuses on delivering the final product to the target audience through various platforms.
Q3: What tools and software are commonly used in digital media production?
Common tools and software include:
Video Editing: Adobe Premiere Pro, Final Cut Pro, DaVinci Resolve.
Audio Production: Pro Tools, Ableton Live, Logic Pro.
Graphic Design: Adobe Photoshop, Adobe Illustrator, InDesign.
3D Modeling and Animation: Blender, Autodesk Maya.Common tools and software include:
Video Editing: Adobe Premiere Pro, Final Cut Pro, DaVinci Resolve.
Audio Production: Pro Tools, Ableton Live, Logic Pro.
Graphic Design: Adobe Photoshop, Adobe Illustrator, InDesign.
3D Modeling and Animation: Blender, Autodesk Maya.


Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.